Material database
The material database in Dyssol stores physical properties and compound information.
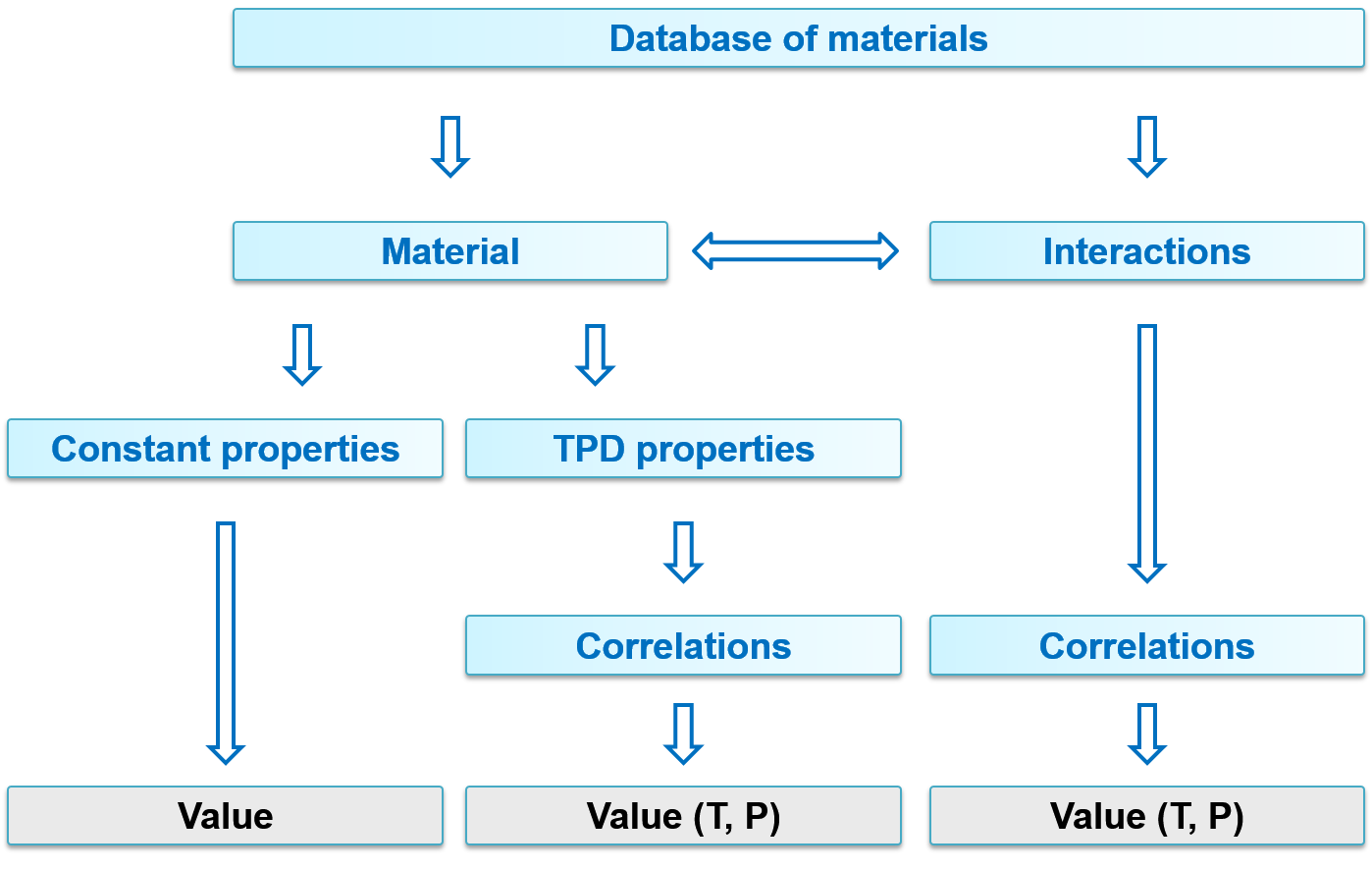
You can find the database structure in the figure below. The compound properties can be constant or T(temperature), P(pressure)-dependent. The dependent properties can be calculated using correlations.
DMDB file
You can find the file Materials.dmdb in your installation folder, which stores global list of materials and their parameters. Typical examples in current database are air, coal, sand, urea and water.
You can extend this database by defining your own new materials using the Tools menu bar → Materials database, which opens the compounds editor and enables you to set new compounds.
Constant parameters
Not all properties have influence on internal calculations. State of aggregation can be used to define several aggregation states of the same material. These parameters can be accessed through units and material streams.
Constant parameters in Dyssol consist of:
Critical pressure
Critical temperature
Heat of fusion
Heat of vaporization
Molar mass: mandatory for simulation, since many parameters are calculated based on it
Normal boiling point
Normal freezing point
Reactivity type
Formation enthalpy
State of aggregation: represented by different numbers. 0 for solid, 1 for liquid, 2 for gas, 3 for unknown
User defined properties
Dependent parameters
Like constant parameters, temperature- and/or pressure-dependent (TPD) parameters can also be accessed through units and material streams.
Dependent parameters in Dyssol consist of:
Density: mandatory for simulation, since it participates in PSD transformations and T-equilibrium
Enthalpy: mandatory for simulation, since it participates in T-equilibrium
Thermal conductivity
Viscosity
Permittivity
Use defined properties
Interaction properties
List of interaction properties:
Interface tension
User defined properties
Correlations
Correlation search
The algorithm for calculating TPD and interaction properties is shown as follows.
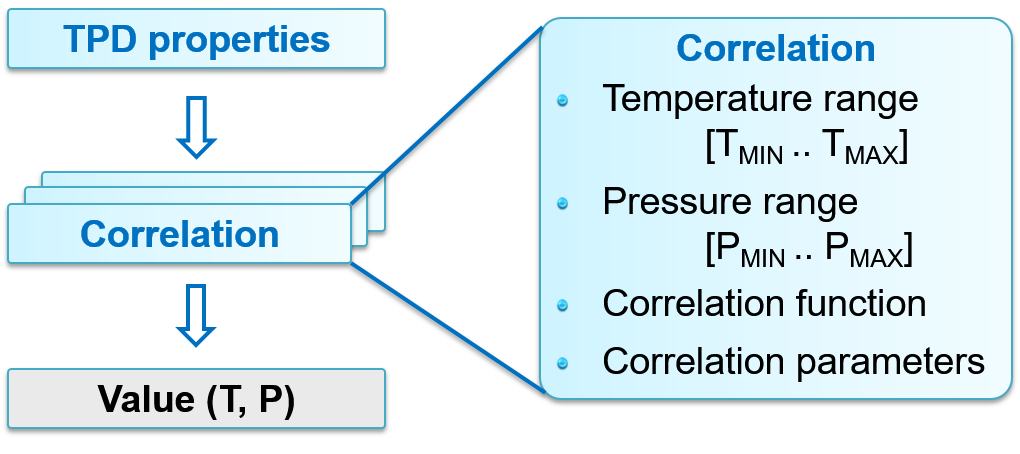
For each T or P range (given in the literature), it consists of 3 steps:
Find the correlation with T & P within the first T or P-range. Calculate value according to the correlation function for this range.
Find the correlation with only T within the first T or P-range. Calculate value according to the correlation function for this range.
Find the nearest correlation, taking only T into account. Perform nearest neighbour extrapolation.
Correlation functions
The correlation functions \(y = f(T,P)\) in Dyssol are listed below. The letters \(a ... f\) are constants. For different temperatur and pressure ranges, different functions should be applied.
Constant:
\(y = a\)
Linear:
\(y = aT + bP + c\)
Exponential:
\(y = a\,b^{c+dT+\frac{eT + f}{gT + h}} + i\)
Power function
\(y = a\,T^b\)
Polynomial:
\(y = a + bT + cT^2 + dT^3 + eT^4 + fT^5 + gT^6 + hT^7\)
Shomate heat capacity:
\(y = a + bT + cT^2 + dT^3 + \frac{e}{T^2}\)
Shomate standard enthalpy:
\(y = aT + b\frac{T^2}{2} + c\frac{T^3}{3} + d\frac{T^4}{4} - \frac{e}{T} + f - g\)
Shomate standard entropy:
\(y = a + \ln T + bT + c\frac{T^2}{2} + d\frac{T^3}{3} - \frac{e}{2T^2} + f\)
List of T-values (user defined):
\(y = \{T1:val1, T2:val2, T3:val3, ...\}\)
List of P-values (user defined):
\(y = \{P1:val1, P2:val2, P3:val3, ...\}\)