Granulator
This unit represents a simplified model of a fluidized bed granulation reactor. The model does not take into account attrition of particles inside the apparatus and does not keep properly any secondary distributed properties except size.
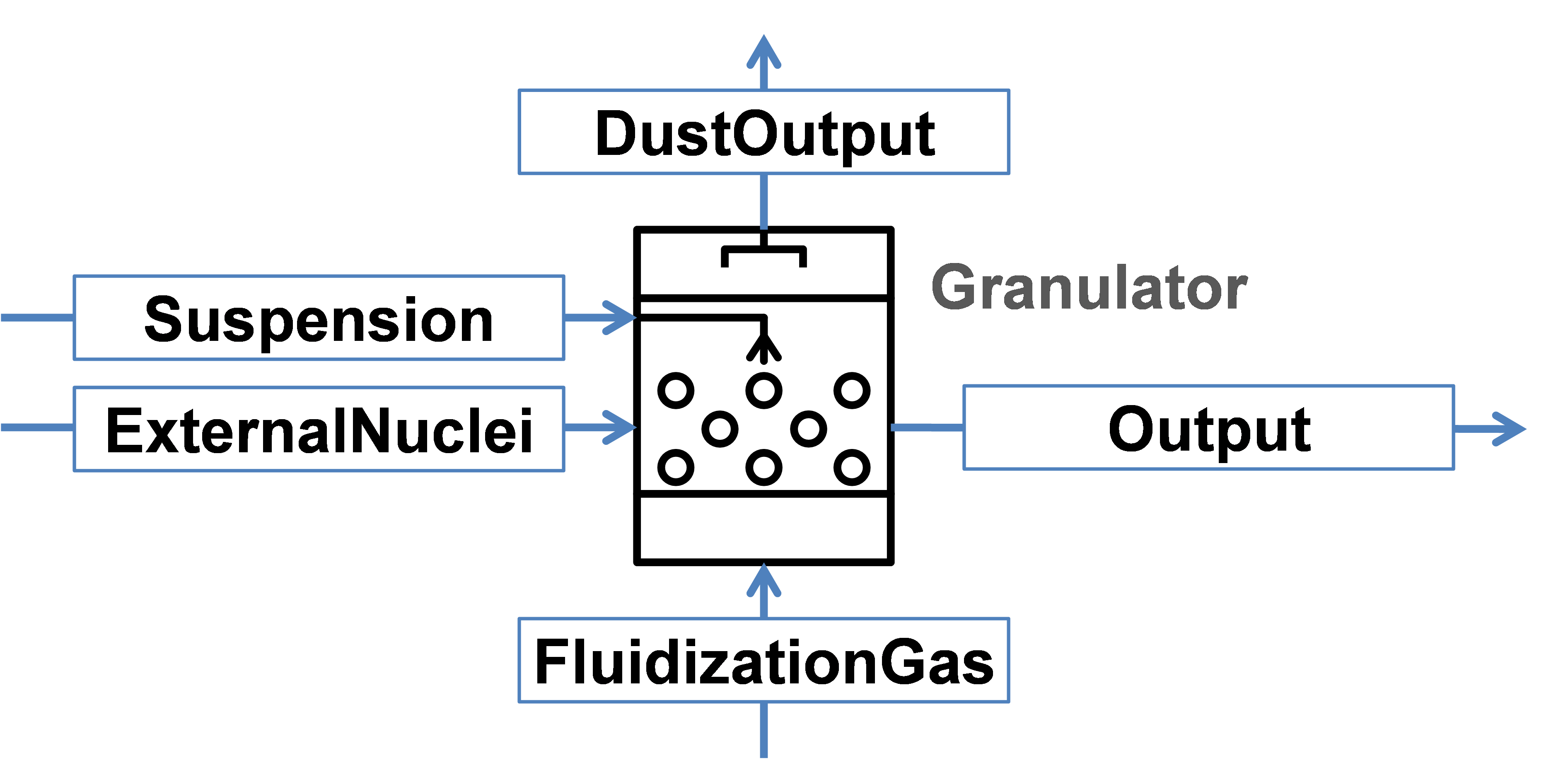
Continuous granulator
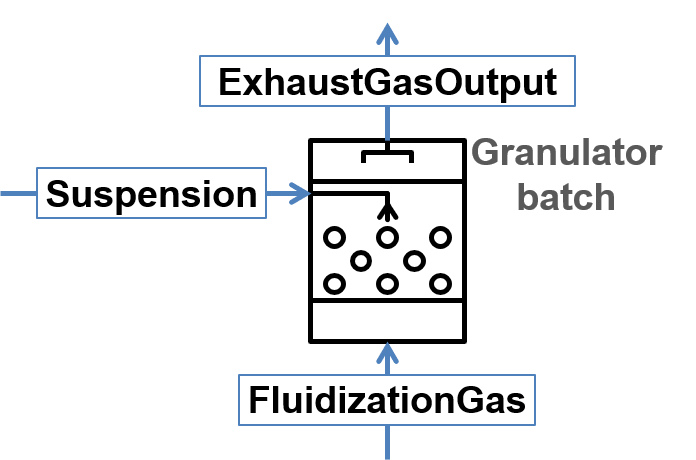
Batch granulator
Note
Notations:
\(q_3\) – mass density distribution of particles inside apparatus
\(q_3^{in}\) – mass density distribution of external particles from ExternalNuclei stream
\(\Delta d\) – class size
\(d_p\) – particle diameter in a class
\(\dot{m}_{in}\) – mass flow of input nuclei
\(\dot{m}_{out}\) – output mass flow of the product
\(\dot{m}_{dust}\) – output mass flow from the DustOutput
\(\dot{m}_{susp}\) – total mass flow of the suspension
\(\dot{m}_{s,susp}\) – mass flow of the solid phase in the Suspension inlet
\(\dot{m}_{fl,g}\) – mass flow of the gas phase in the FluidizationGas inlet
\(\dot{m}_{exh}\) – output mass flow from the ExhaustGasOutput
\(\dot{m}_{e}\) – effective mass stream of the injected suspension
\(\dot{m}_{gran,liq}\) – liquid mass flow leaving the granulator with granules
\(\dot{m}_{in,liq}\) – total effective mass flow of liquid
\(\dot{m}_{sus,liq}\) – mass flow of the liquid phase in the Suspension inlet
\(\dot{m}_{nuc,liq}\) – mass flow of the liquid phase in the ExternalNuclei inlet
\(\dot{m}_{gas,liq}\) – mass flow of the liquid phase in the FluidizationGas inlet
\(M_{tot}\) – holdup mass
\(u_{moist}\) – moisture content of granules (dry basis)
\(\rho_{s,susp}\) – density of solids in the holdup
\(G_{e}\) – effective growth rate
\(A_{tot}\) – total surface of particles in the granulator
\(K_{os}\) – overspray part in the suspension
Note
particle size distribution is required for the simulation. This unit is applied for solid, liquid and gas phases.
Note
Input parameters needed for the simulation:
Name |
Symbol |
Description |
Units |
Boundaries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Kos |
\(K_{os}\) |
Overspray part in the suspension |
[–] |
0 ≤ \(K_{os}\) ≤ 1 |
Granules moisture content |
\(u_{moist}\) |
Moisture content of granules (dry basis) |
[–] |
0 ≤ \(u_{moist}\) |
Relative tolerance |
– |
Relative tolerance for equation solver |
[–] |
0 < RTol ≤ 1 |
Absolute tolerance |
– |
Absolute tolerance for equation solver |
[–] |
0 < ATol ≤ 1 |
Note
State variables:
Name |
Symbol |
Description |
Units |
|---|---|---|---|
Atot |
\(A_{tot}\) |
Total surface of particles in the granulator |
[\(m^2\)] |
Mtot |
\(M_{tot}\) |
Total mass of all particles in the granulator |
[kg] |
Mout |
\(\dot{m}_{out}\) |
Output mass flow of the product |
[kg/s] |
Mdust |
\(\dot{m}_{dust}\) |
Output mass flow of dust |
[kg/s] |
G |
\(G_{e}\) |
Effective growth rate |
[m/s] |
PSDi |
\(q_{3,i}\) |
Mass density distribution of particles |
[1/m] |
See also
a demostration file at Example Flowsheets/Units/Granulator.dlfw.
See also
S.Heinrich, M. Peglow, M. Ihlow, M. Henneberg, L. Mörl, Analysis of the start-up process in continuous fluidized bed spray granulation by population balance modelling, Chem. Eng. Sci. 57 (2002) 4369-4390.